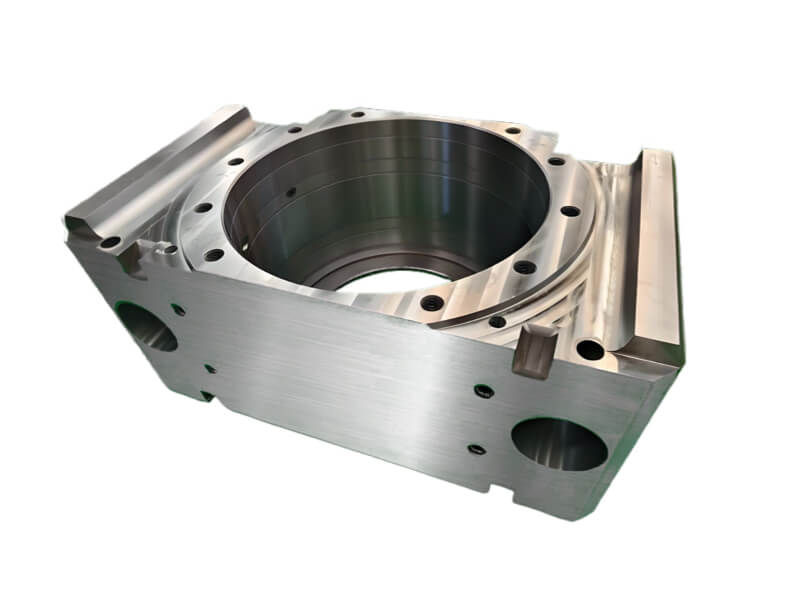
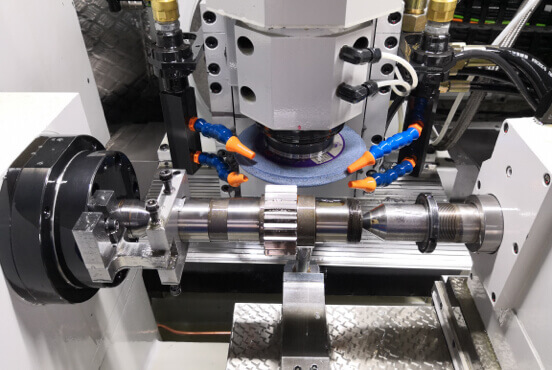
Machining Parts Description
Machining involves removing material from a workpiece to achieve the desired shape, size, and surface finish, utilizing various techniques such as turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). These processes are typically carried out on advanced machining equipment, including computer numerical control (CNC) machines, which ensure high levels of accuracy and repeatability. Machining allows for the fabrication of parts made from a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, catering to diverse application requirements.
Machining parts are components produced through various machining processes, including turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). These processes involve the removal of material from a workpiece to achieve desired dimensions, properties, and surface finishes.
Manufacturing Method of Machining Parts

Turning
Rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool to remove material and create cylindrical parts.

Milling
Using rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, allowing for complex shapes and features.

Drilling
Creating holes in parts with high precision.

Grinding
Finishing process that removes small amounts of material to achieve exact dimensions and surface finish.

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Uses electrical discharges to remove material from a conductive workpiece, ideal for complex shapes.
Material of Machining Parts
The choice of material for precision machining parts is critical, as it affects the performance, durability, and application of the components. Here’s a list of commonly used materials in precision machining:
01
Aluminum Alloys
Properties
Lightweight, good corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability.
Applications
Aerospace components, automotive parts, and consumer electronics.
02
Steel Alloys
Types
Carbon Steel: High strength and toughness; used in general applications.
Alloy Steel: Enhanced properties for specific applications (e.g., tool steels, stainless steel).
Applications
Gears, shafts, and structural components.
03
Stainless Steel
Properties
Excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
Grades
Common grades include 304, 316, and 440.
Applications
Medical devices, food processing equipment, and outdoor applications.
04
Brass
Properties
Good machinability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Applications
Valves, fittings, and decorative components.
05
Copper
Properties
Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity.
Applications
Electrical components, heat exchangers, and plumbing fittings.
06
Plastics
Types
Polycarbonate: High impact resistance.
Acrylic: Good optical clarity and machinability.
PTFE (Teflon): Excellent chemical resistance.
Applications
Enclosures, insulators, and low-friction components.
07
Titanium Alloys
Properties
High strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance.
Applications
Aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts.
06
Composites
Materials Reinforced plastics (e.g., carbon fiber, fiberglass).
Properties
Lightweight and high strength.
Applications
Aerospace components and high-performance sporting goods.